What is a Website?
Before learning about website developers, it’s important to know what a website is.
A website is a collection of web pages that are linked together to form a cohesive space on the internet. These pages can contain text, images, videos, and other types of content.
The purpose of a website is to help businesses establish their brand identity and offer a way to communicate with customers. Websites are also powerful tools for lead generation, encouraging users to take action.
A website developer creates, builds, and maintains websites using coding languages, tools, and web technologies, ensuring functionality and performance across browsers and devices.
The key skills a web developer needs include HTML, CSS, JavaScript, frameworks like React or Django, and soft skills like communication, problem-solving, and collaboration. These abilities help them manage both front-end design and back-end logic to deliver complete and scalable websites.
The different types of website developers are front-end, back-end, and full-stack, as well as specialized roles like WordPress developers, e-commerce developers, and CMS experts. Each type contributes uniquely, depending on the project’s technical and design needs.
Website developers earn between £25,000 and £100,000+ annually in the UK. Freelance developers charge £25–£100/hour depending on experience, niche, and scope. Salaries vary based on region, role, and technology stack.
You can hire a website developer in the UK through platforms like Onexcell, Upwork, PeoplePerHour, or by connecting with local web agencies in London, tech job boards, or in-person networking events. The best choice depends on your project timeline, complexity, and budget.
What Is A Website Developer?
A website developer is a digital professional who builds, maintains, and optimizes websites using coding languages, frameworks, and various development tools. They write the behind-the-scenes code that turns a visual design into a working, interactive site, ensuring it runs smoothly across devices and browsers.
As a core player in the web development field, a website developer plays a hands-on role in shaping how users experience the internet. They do these through basic websites, advanced web apps, or full-scale e‑commerce platforms.
This developer role blends elements of software development, problem-solving, and technical implementation, and it’s essential in today’s digital economy. Businesses of all sizes rely on web developers to build scalable, secure, and performance-optimized platforms that connect them with users.
Unlike DIY website builders, a professional web developer customizes solutions to specific goals using structured code and best practices in web technology. They are more than just “website builders,” but rather coding professionals and web development experts who understand both the frontend and backend of digital systems.
What Does A Website Developer Do?
The things a website developer does include writing code, building website structures, and integrating functionalities like forms, databases, or payment gateways. They also test and debug websites, optimize performance, and ensure that everything runs smoothly across browsers and devices as part of broader web development services.
Below are the core web developer responsibilities:
- Planning and Requirements Gathering: They consult with clients or stakeholders to understand client requirements, project goals, and functionality needs. This early step sets the technical scope and timeline for the full web project delivery.
- Coding and Site Construction: Developers write code to build the website structure and functionality, using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and other languages. They create responsive layouts, develop user interactions, and integrate tools like content management systems or third-party APIs. This is the core of coding websites.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: They run cross-browser and cross-device website testing to catch bugs and usability issues. This includes checking load speed, security, accessibility, and ensuring that user flows work as intended.
- Troubleshooting and UX Improvement: When bugs or broken features appear, developers efficiently debug and resolve them. They also improve UX (user experience) by adjusting layouts, fixing interface glitches, and optimizing performance based on user feedback or analytics data.
- Ongoing Maintenance and Updates: Even after launch, developers handle updates, backups, and security patches. They maintain the site’s health and reliability over time, especially for dynamic platforms like e-commerce or web applications.
These responsibilities make website developers essential for not just building, but also evolving digital platforms to meet changing user and business needs.
How Is A Website Developer Different From A Web Designer?
A website developer is different from a web designer in terms of focus, skillset, and the tools they use. While both contribute to building a website, they approach the process from different angles. Developers handle the code and functionality, while designers focus on layout, visuals, and user experience (UX/UI). Understanding the web designer vs developer distinction helps clarify team roles and project expectations.
Here are the key differences between a website developer and a web designer:
Web developers focus on the following:
- Writing code for site functionality (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP)
- Database integration and back-end logic
- Website performance and interactivity
- Implementing CMS or web applications
Website designers focus on the following:
- Visual design, typography, and color schemes
- Layout composition and front-end styling
- UX/UI flow and responsive design
- Using tools like Figma, Adobe XD, or Sketch
In short, design vs code defines the core difference, but successful web projects require tight collaboration between these roles to align both visual design and functional performance.
What Are The Key Skills A Website Developer Needs?

The key skills a website developer needs are a mix of technical expertise and soft skills, from coding languages like HTML and JavaScript to communication and problem-solving. Success in web development relies on both building functional, responsive websites and being able to work effectively with teams, clients, and evolving technologies.
Here are the essential skills a website developer needs:
1. Technical Skills:
- HTML & CSS: These are the building blocks of web pages. HTML defines the structure, while CSS controls visual styling, layout, and responsiveness.
- JavaScript: Enables interactivity and dynamic elements like sliders, modals, and real-time updates. It is critical for both front-end development and modern web apps.
- Frameworks and Libraries (e.g., React, Vue, Bootstrap): Help streamline development and enforce best practices in design and code efficiency.
- Back-End Skills (e.g., Node.js, PHP, Python): Useful for handling databases, user authentication, and server-side logic. It is essential in full-stack or back-end roles.
- Database Management (e.g., MySQL, MongoDB): Enables the developer to store, retrieve, and manage data effectively for web applications and CMS-driven sites.
- Responsive Design: Ensures websites work smoothly on all screen sizes, a must-have skill given mobile-first user behavior.
2. Soft Skills:
- Problem-Solving: Developers debug code, fix unexpected errors, and troubleshoot functionality. This is core to daily work and long-term success.
- Communication in Tech: Developers must explain technical issues clearly to non-technical stakeholders and collaborate effectively with designers, marketers, and clients.
- Teamwork Skills: Whether in-house or remote, web developers rarely work alone. Strong collaboration habits improve project flow and reduce miscommunication.
Mastering this combination of coding skills, front-end and backend techniques, and interpersonal abilities positions a website developer for long-term success in both freelance and agency environments.
Need to ask Something else?
Use the form here to send us your question. We’ll reply within one business day.
Send Your Enquiry →What Programming Languages Do Website Developers Use?
The programming languages website developers use are HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, Python, Ruby, and Java, each serving specific purposes in front-end and back-end development. Developers also rely on popular JavaScript frameworks and back-end libraries to build interactive, scalable, and secure web applications across all industries.
Here’s a breakdown of the core programming languages website developers use:
1. Front-End Languages:
- HTML5: Forms the structural backbone of every webpage. Developers use it to define elements like headings, text, images, links, and layout containers.
- CSS3: Controls the styling of colors, fonts, spacing, and responsiveness of a website. It’s essential for front-end developers focused on UI and user experience.
- JavaScript: Adds interactivity like dropdowns, popups, sliders, and dynamic content updates. Used with JavaScript frameworks like React, Vue, or Angular for building single-page applications and complex UIs.
2. Back-End Languages:
- PHP: Widely used for server-side scripting and PHP development in platforms like WordPress. Great for managing form submissions, user authentication, and dynamic content.
- Python: Gaining popularity due to its simplicity and powerful web frameworks like Django and Flask. Common in startups and tech companies building scalable web apps.
- Ruby: Known for its elegant syntax, it is often used with Ruby on Rails for rapid development. Great for MVPs and content-driven sites.
- Java: Often used in enterprise-level web applications for large-scale projects that require stability, multi-threading, and integrations.
- SQL: Used for database querying and management in nearly every web application. Developers rely on SQL to store, update, and retrieve user and system data.
3. Frameworks & Libraries:
- React: A JavaScript library for building fast, reusable UI components.
- Angular: A full-featured front-end framework ideal for complex apps.
- Laravel: A PHP framework known for clean syntax and robust features.
- Django: A secure, scalable Python framework used in large applications.
Each of these technologies plays a role in delivering websites that are fast, secure, and easy to use. Whether you’re working on a portfolio site, an e-commerce website development project, or a full-scale web application development system, these languages are necessary.
What Are The Types Of Website Developers?
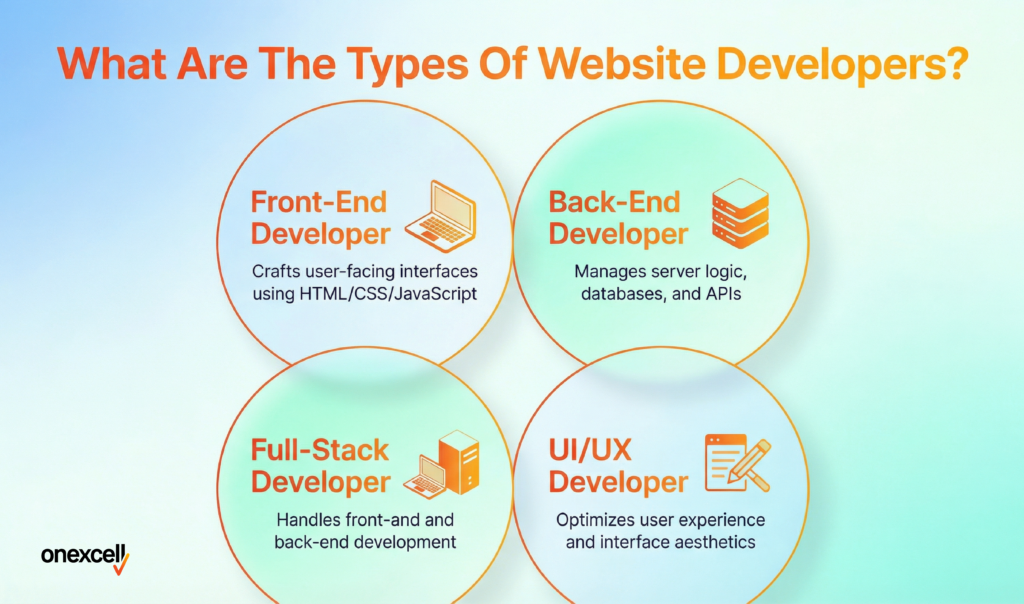
The types of website developers are front-end developers, back-end developers, and full-stack developers, each specializing in different parts of the website development process. In addition to these core categories, there are CMS specialists, e-commerce developers, and mobile web developers who focus on specific platforms or technologies.
Understanding these roles helps you choose the right developer for your simple business site, a custom web application, or a high-volume e-commerce platform.
The types of website developers are explained below:
- Front-End Developers: These developers handle everything users see and interact with on a website. They work with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to build layouts, animations, and responsive elements, often collaborating with designers to bring mockups to life.
- Back-End Developers: Focused on server-side logic, databases, and APIs, these developers build the infrastructure that powers dynamic content and user interactions. They ensure that data flows smoothly and securely between users, servers, and applications.
- Full-Stack Developers: Skilled in both front-end and back-end technologies, full-stack developers can handle end-to-end web development. They’re especially valuable for startups or smaller teams that need broad technical coverage.
- CMS Specialists (e.g., WordPress Developers): These developers build and customize websites using content management systems like WordPress, Joomla, or Drupal. They often handle theme development, plugin customization, and CMS migrations.
- E-Commerce Developers (e.g., Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento): Focused on e-commerce website development, these specialists create and maintain online stores, implement shopping carts, set up payment gateways, and optimize checkout experiences.
- Mobile Web Developers: These developers focus on optimizing websites for mobile performance and usability. They may also work with progressive web apps (PWAs) or responsive frameworks to deliver a seamless experience across devices.
Each developer type plays a key role in modern web development, and the right combination depends on your site’s complexity, budget, and goals.
What Is The Difference Between Front-End, Back-End, And Full-Stack Website Developers?
Front-end, back-end, and full-stack website developers each specialize in different parts of the web development process. A front-end developer focuses on UI development and design —they write code using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to build the visual parts of a website that users interact with, such as buttons, forms, and responsive layouts. Their job includes responsive design coding, making sure the site looks and functions properly across devices.
On the other hand, a back-end developer handles the server-side coding, logic, and database integration that power a website’s functionality behind the scenes. They write scripts in languages like PHP, Python, or Node.js to manage user logins, form submissions, content updates, and dynamic content. Back-end developers also create and maintain API connections that allow different systems, like payment gateways or third-party tools, to communicate with the site.
A full-stack developer bridges both roles and can handle the entire full-stack workflow—from building the user interface to setting up databases and deploying servers. For web example and ideas, in an e-commerce project, the front-end developer might code the product display page, the back-end developer handles inventory logic and order processing, and the full-stack developer ensures everything works together smoothly from end to end.
All three roles work together to bring a complete website to life. The front-end handles what users see, the back-end manages what users don’t, and full-stack developers fill in the gaps to ensure speed, stability, and functionality.
How Do You Become A Website Developer From Scratch?
To become a website developer from scratch, start by learning the basics of HTML and CSS, which are the foundation of any webpage. Once you understand how to build static pages, move on to JavaScript to add interactivity, and then explore JavaScript frameworks like React or Vue to build more advanced applications. Understanding basic version control using Git and GitHub is also essential for modern development.
As you progress, start building real-world projects, such as landing pages, portfolios, or basic web apps, to apply what you’ve learned and show your skills. Eventually, compile your best work into a developer portfolio, which is crucial when applying for jobs or freelance gigs.
The following are ways to become a web developer:
- Online platforms like FreeCodeCamp, Codecademy, and The Odin Project offer structured lessons.
- Coding bootcamps such as Le Wagon, General Assembly, and CareerFoundry provide immersive, career-focused training in web development.
- You can also take the self-taught web developer path by combining YouTube tutorials, technical blogs, and trial-and-error practice.
The web developer roadmap isn’t one-size-fits-all, but consistency, curiosity, and real coding experience are what truly move you forward. Whether you enroll in a web development training program or teach yourself online, building a strong foundation in both front-end and back-end skills will prepare you for a successful career.
Can You Become A Website Developer Without A Degree?
Yes, you can absolutely become a website developer without a degree. What matters most is your skills, portfolio, and real-world experience. Employers and clients in tech value what you can do over where you went to school, especially in roles like web development, where your portfolio speaks louder than a résumé.
There are many ways to break into the field without a formal education. You can enroll in online coding courses (like FreeCodeCamp, Coursera, or Scrimba), join a coding bootcamp, or follow structured tutorials to teach yourself front-end and back-end skills.
How Much Does A Website Developer Earn?
A website developer’s salary ranges from £25,000 to £70,000. It can vary widely depending on their experience level, location, and specialization within the tech industry. On average, junior developers earn between £25,000–£35,000 per year in the UK and $50,000–$70,000 globally, while mid-level developers make £40,000–£60,000 or $75,000–$100,000 depending on their stack and company type.
Senior developers with 5+ years of experience and advanced skills (like full-stack expertise or e-commerce development) can earn over £70,000 in the UK and $120,000+ in high-paying markets like the U.S., Canada, or Western Europe.
Freelancers operate under different models; freelance web developer rates range from £25 to £100 per hour, depending on their niche, portfolio strength, and project type. A WordPress freelancer may charge £40/hour, while a Shopify or React developer could charge £80/hour or more for specialized tasks.
Overall, developer income continues to rise as demand for web development services grows. Whether working in-house, remotely, or as a freelancer, skilled developers are well-compensated across most markets.
How Do You Hire The Right Website Developer For Your Project?
You hire the right website developer for your project by having a clear understanding of your project goals, timeline, and technical requirements. Beyond technical skills, the ideal developer should also align with your communication style, business priorities, and long-term expectations. Whether you’re hiring for a freelance project or a full-time role, a structured evaluation process is essential to avoid mismatches and costly delays.
The following are tips to hire the right web developer for your projrct:
- Developer Portfolio Review: Examine past projects similar to your own, look for design quality, functionality, and performance. A strong portfolio should reflect hands-on experience with the tools and features your site requires, such as responsive layouts, e-commerce functionality, or CMS customizations.
- Technical Interview Questions: Ask about their coding process, debugging methods, and familiarity with relevant stacks (e.g., WordPress, Laravel, React). Tailor questions to the role (front-end, back-end, or full-stack), and include scenario-based challenges if needed.
- References and Testimonials: Always request references or client feedback. Previous clients provide insight into reliability, timeliness, and ability to collaborate under pressure.
- Project Fit Assessment: Assess their understanding of your business goals and ability to translate them into technical execution. A great developer asks smart questions about your users, brand, and growth plans.
- Communication and Availability: Clear, proactive communication is critical, especially for remote or freelance roles. Developers should be comfortable using tools like Trello, Slack, or Google Docs to provide updates and respond to change requests.
In short, hiring a web developer is not just about code; it’s about fit, clarity, and trust. When evaluating developers, prioritize those who show strong problem-solving skills, technical depth, and a proven ability to deliver web projects on time and on spec.
Where Do You Hire A Website Developer In The UK?

You can hire a website developer in the UK by exploring a mix of freelance platforms, local agencies, and UK-specific job boards or events, depending on your budget, project size, and support needs.
Here are some of the most effective places to find skilled website developers in the UK:
- Onexcell: Onexcell is a UK-based web development agency that provides professional web development services tailored to businesses of all sizes. The benefit of hiring through an agency like Onexcell is access to a vetted team, structured project management, and ongoing support. While agency rates are typically higher than freelancers, you gain stability, communication, and a long-term partnership that many businesses prefer for strategic projects.
- Upwork: Upwork is a global freelance marketplace where you can post jobs and hire from a pool of developers worldwide, including many in the UK. It offers flexibility in rates, detailed profiles, and payment protection. However, the platform can be time-consuming to vet applicants, and the quality can vary widely if you’re not familiar with evaluating developers.
- PeoplePerHour UK: A UK-specific freelance platform, PeoplePerHour makes it easier to find local talent who understand the market and timezone. It’s ideal for small businesses seeking a UK freelance web developer, but pricing can be inconsistent and highly competitive, often driving rates below market value for complex work.
- Web Agencies in London and Major Cities: Searching for “web agencies London” or similar local firms gives you access to in-person consultation, faster communication, and GDPR-compliant handling of UK-based data. The downside is that these services tend to have longer onboarding timelines and higher overhead costs.
- UK Tech Job Boards (e.g., CWJobs, Technojobs, Jobserve): These platforms are excellent for permanent hires or contract-based roles. You get access to qualified applicants, but you’ll need to manage outreach, screening, and project management yourself.
- Local Networking & Meetups (e.g., London Web Meetups, Tech Nation Events): Attending UK web development events or regional startup gatherings is a great way to meet developers face-to-face. While this method takes longer, it often results in stronger, trust-based working relationships.
Whether you’re after a freelancer, an in-house hire, or a full-service team, Onexcell UK offers reliable web development. The best platform depends on your project scope, budget, and whether you value speed, cost-efficiency, or managed service.
Can AI Replace Website Developers?
No, AI cannot fully replace website developers, at least not yet. While tools like ChatGPT, Copilot, and other AI web development platforms assist with code generation, layout suggestions, and even basic logic, they cannot fully understand business goals, user context, or deliver production-ready, secure, and scalable solutions without human oversight.
Complex tasks like database architecture, debugging, performance optimization, and understanding nuanced UX decisions still require human experience, collaboration, and judgment.
That said, the future is likely to be hybrid. AI will continue to improve and may automate repetitive coding tasks, especially with the rise of no-code tools, automation in coding, and smart UI builders. In short, when it comes to AI vs human developers, the near future belongs to those who know how to use both.
Do Website Developers Also Handle Website Maintenance?
Yes, many website developers offer ongoing maintenance services as part of their long-term engagement with clients. After a site goes live, developers are often responsible for handling website updates, fixing bugs, optimizing performance, and ensuring compatibility with new browsers or devices.
Maintenance also includes security patches, monitoring uptime, backing up data, and occasionally rolling out new features based on user feedback or changing business needs.
What Role Does A Website Developer Play In Website Security?
Website developers play a critical role in securing websites through secure coding practices, regular updates, and proactive defense mechanisms. They are responsible for building secure web applications from the ground up, writing clean, validated code that prevents common vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and insecure file uploads.
Developers also integrate SSL certificates to encrypt data transmission and ensure all communications between the browser and server are secure.
Beyond development, experienced coders implement data encryption for user credentials, build secure login systems with password hashing, and conduct security testing to identify weaknesses. Regular code audits, permission controls, and the use of frameworks with built-in security help strengthen defense.
What Is The Difference Between Freelance And In-House Website Developers?
A freelance developer works independently on a contract basis, typically managing multiple clients and setting their own schedules. Freelancers offer flexibility, lower long-term cost, and are ideal for outsourcing web projects with a clear scope and deadline—like building a landing page, updating a WordPress theme, or launching an MVP. However, they may have limited availability for urgent tasks, and the consistency of support can vary depending on workload and communication habits.
An in-house developer is a full-time employee embedded within your organization. They’re ideal for companies that need ongoing updates, tight collaboration, or high-security standards—such as in SaaS products or large e-commerce platforms. While they cost more in terms of salary and benefits, the advantage is deep product familiarity, faster iteration, and alignment with your long-term goals.
What Certifications Can Help A Website Developer’s Career?
The certifications that can help a website developer’s career include Google Mobile Web Specialist, AWS Certified Developer, Microsoft Certified: Azure Developer Associate, and other online tech certifications that validate both front-end and back-end development skills.
While not mandatory, these web development certifications help build trust with clients, improve credibility in job applications, and sometimes unlock access to higher-paying roles or contracts.
The certifications that help a website developer’s career:
- Google Mobile Web Specialist: This certification tests a developer’s ability to build responsive, mobile-friendly web apps. It’s ideal for front-end developers who want to demonstrate real-world skills in HTML5, JavaScript, performance optimization, and progressive web apps.
- AWS Certified Developer – Associate: This certification is valuable for back-end or full-stack developers working on cloud-based applications. It proves your ability to build, deploy, and maintain scalable web solutions using Amazon Web Services (AWS).
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Developer Associate: Similar to the AWS path, this credential validates your skills in building web applications using Microsoft Azure, focusing on serverless computing, APIs, and database integration. It’s well-suited for developers working with enterprise clients or Microsoft stacks.
- freeCodeCamp, Coursera, and Codecademy Certificates: While not as recognized as vendor-specific credentials, these online coding credentials show your commitment to learning. They help entry-level developers break into the field, especially in freelance or startup settings.
Certifications alone won’t land you a job, but they strengthen your profile, especially when paired with a strong portfolio. In a competitive market, recognized coding credentials can be the extra layer of assurance that makes a client or hiring manager say yes.

